As the world rapidly adapts to huge technological advancements, the traditional way of handling money has completely transformed. The rise of cryptocurrencies and development of CBDCs (Central bank digital currencies) have sparked a financial revolution, shaping the future of financial systems worldwide.
Cryptocurrencies are completely digital and can be used as an alternative form of payment. They are created using encryption algorithms that ensure their security and run on decentralised digital ledgers called blockchains, which record and verify all transactions across many computers in a network. Unlike typical ways of payment, such as cash, debit or credit cards, cryptocurrency doesn’t require a bank to verify transactions, resulting in increased speed, accessibility, and privacy. Popular examples of cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin and Ethereum. On the other hand, CBDCs are the digital form of government issued currencies, and are used to support financial services and ensure national economic stability by offering wider access to central bank money and having the ability to set official interest rates. CBDCs modernise financial systems whilst ensuring they are still regulated by the central bank and government, ensuring legal compliance. Examples of CBDCs are the Sand Dollar (Central Bank of Bahamas) and eNaira in Nigeria.
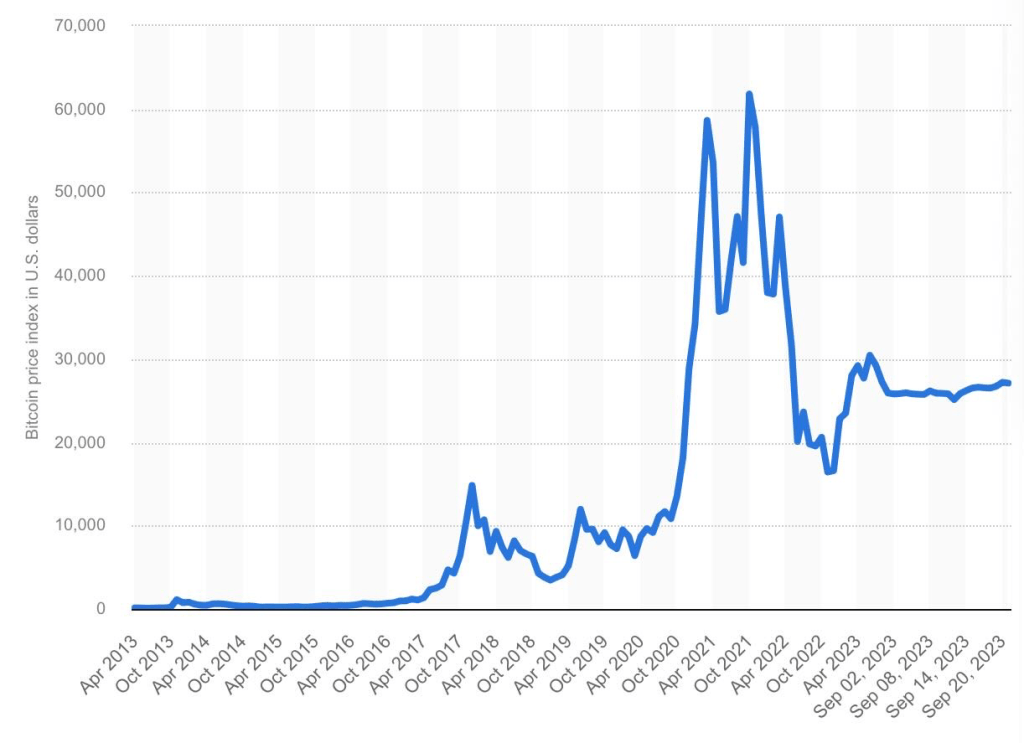
The rise of cryptocurrency has earned worldwide attention and they have become a popular way to invest in recent years. This popularity is defined in the incredible growth of Bitcoin, from $0.06 on September 29th 2010, to $27000 thirteen years later. This extreme rise in value is due to supply and demand: due to there being an extreme, sudden demand but a minimal supply it caused an incredible increase in price. In contrast to many other cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin has a finite supply of 21 million coins, with 19 million already being mined, and in possession, making it an even more scarce asset further propelling its value. Over the past 13 years, the wider acceptance of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as a means of payment between citizens, has made them mainstream, solidifying cryptocurrencies as a big part of our financial future.
CBCDs are also rapidly emerging as the future of banking, with 11 countries already having implemented them, 53 in advanced planning stages and 46 actively researching them as of June 2023 according to Statista. Countries are engaging with this, because CBDCs are digital versions of fiat currencies and have the potential to improve the efficiency of payments, granting easier access and increased transfer speeds, providing central banks greater control over monetary policy. However, it is important to recognise the implementation of CBDCs is still in its early stages, and as higher GDP countries adopt CBDCs and they become more popular, it is likely that over the next decade there will be a huge amount of data and opinions on them.
In this new era of digital currencies, it is exciting to note their many benefits, yet equally important to highlight the challenges they bring. Due to the digital natures of cryptocurrencies and CBDCs, they bring the potential for hacking and fraudulent activities which pose significant risks to the usage of these currencies. Additionally, cryptocurrencies are decentralised which means they can facilitate illegal activities that involve the transmission of monetary value. As well as being a potential hub for criminals, price fluctuations of cryptocurrencies add a layer of uncertainty to investors, with a study in Nov 2022 revealing approximately 75% of users that had bought Bitcoin lost money, prompting questions about their stability in supporting an economy. Alongside these concerns, CBDCs allow increased financial surveillance for banks at the expense of citizen privacy, meaning every transaction becomes accessible to government agencies. These disadvantages cast a shadow of uncertainty over the future of digital money and its safety.
The underlying technology of digital currencies, blockchains, has sparked waves of innovation across many industries, offering many uses beyond finance. Its decentralised nature is useful in supply chain management, ensuring transparency and traceability from the source of raw materials to its end products. This allows companies to combat counterfeiting, by being able to follow the whole process, enhancing consumer trust. Blockchains are also extremely useful in healthcare, due to their secure and immutable ledgers, they can be the foundation for patient data management, granting patients greater control over their health records and healthcare providers accurate and up to date information securely. Another potential usage of blockchain technology is in voting systems, as they could enhance election security (voter privacy and legitimacy), eliminate voter fraud, and increase accessibility for citizen participation. An illustrative example is The FDA’s partnership with IBM in June 2019, leading to the development of a blockchain based system to track pharmaceuticals, enhancing drug safety. Estonia’s e-residency programme, launched at the end of 2014, leverages blockchain for secure digital identities, allowing entrepreneurs worldwide to have EU-based businesses. These examples highlight the potential for cryptocurrencies and CBDCs, driven by blockchain technology, in revolutionising industries around the world.
In summary, the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies and CBDCs point to the future of global financial systems. These digital innovations challenge conventional financial norms, while taking on diverse forms of money. The impact of cryptocurrencies and CBDCs extend beyond financial transactions; they redefine the roles of traditional banking institutions, initiating their adaptation to an ever-changing financial landscape. As we move forward into a new era for money, these currencies, driven by the power of blockchain technology, will likely play a pivotal role in shaping our society in the future.


Very well written Jaymiel
LikeLike
Very informative and well presented. This article really gives an insight to Cryptocurrencies and CBDCs.
LikeLike
Very interesting write up. I really enjoyed the detailed explanation 👏
LikeLike